Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Docosahexanoic Acid Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Apoptosis by Autophagy Upregulation via GPR120/mTOR Axis in Insulin-Secreting Cells
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):353-363. Published online January 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1809
- 901 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) reportedly have protective effects on pancreatic β-cells; however, the underlying mechanisms are unknown.
Methods
To investigate the cellular mechanism of PUFA-induced cell protection, mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells were cultured with palmitic acid (PA) and/or docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alterations in cellular signaling and apoptosis were examined.
Results
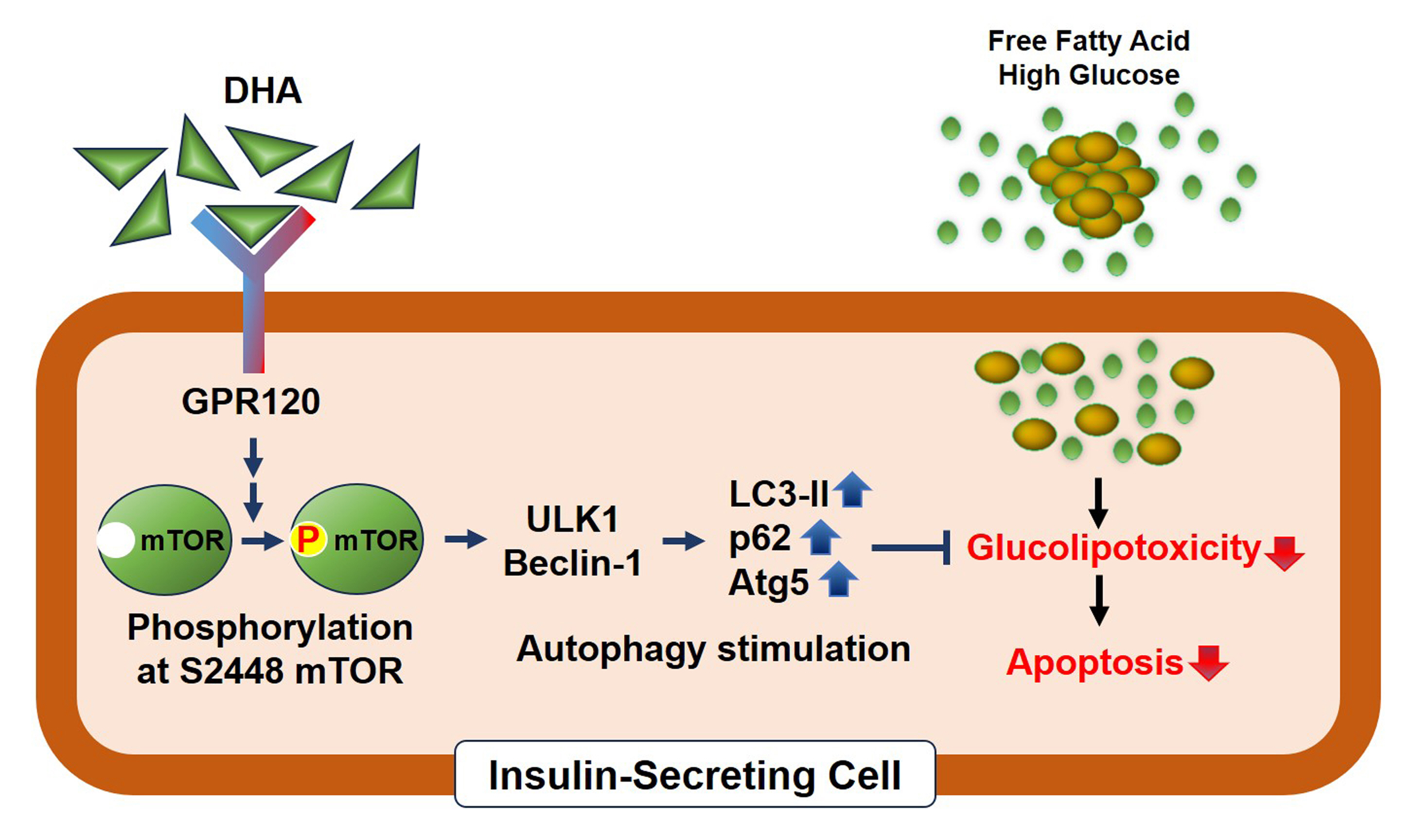
DHA treatment remarkably repressed caspase-3 cleavage and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive red dot signals in PA-treated MIN6 cells, with upregulation of autophagy, an increase in microtubule- associated protein 1-light chain 3 (LC3)-II, autophagy-related 5 (Atg5), and decreased p62. Upstream factors involved in autophagy regulation (Beclin-1, unc51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 [ULK1], phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin [mTOR], and protein kinase B) were also altered by DHA treatment. DHA specifically induced phosphorylation on S2448 in mTOR; however, phosphorylation on S2481 decreased. The role of G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) in the effect of DHA was demonstrated using a GPR120 agonist and antagonist. Additional treatment with AH7614, a GPR120 antagonist, significantly attenuated DHA-induced autophagy and protection. Taken together, DHA-induced autophagy activation with protection against PA-induced apoptosis mediated by the GPR120/mTOR axis.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that DHA has therapeutic effects on PA-induced pancreatic β-cells, and that the cellular mechanism of β-cell protection by DHA may be a new research target with potential pharmacotherapeutic implications in β-cell protection.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 during Serum Deprivation Increases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO Signaling Pathway
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Yu-Mi Lim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):98-108. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1786
- 1,399 View
- 80 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) mediates glucose reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules, and SGLT2 inhibitors are used as therapeutic agents for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study aimed to elucidate the effects and mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibition on hepatic glucose metabolism in both serum deprivation and serum supplementation states.
Methods
Huh7 cells were treated with the SGLT2 inhibitors empagliflozin and dapagliflozin to examine the effect of SGLT2 on hepatic glucose uptake. To examine the modulation of glucose metabolism by SGLT2 inhibition under serum deprivation and serum supplementation conditions, HepG2 cells were transfected with SGLT2 small interfering RNA (siRNA), cultured in serum-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium for 16 hours, and then cultured in media supplemented with or without 10% fetal bovine serum for 8 hours.
Results
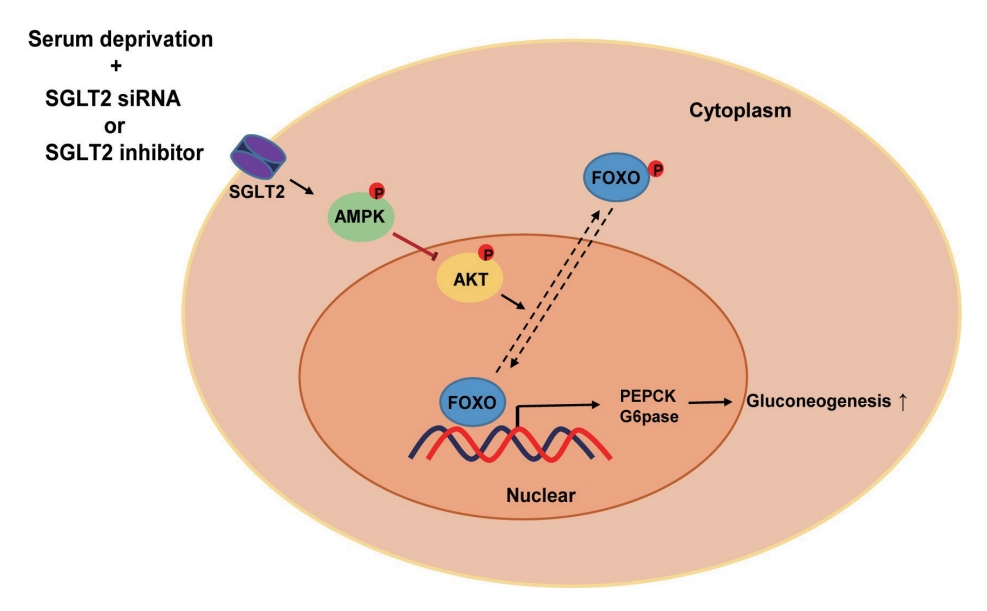
SGLT2 inhibitors dose-dependently decreased hepatic glucose uptake. Serum deprivation increased the expression levels of the gluconeogenesis genes peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1 alpha (PGC-1α), glucose 6-phosphatase (G6pase), and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), and their expression levels during serum deprivation were further increased in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA. SGLT2 inhibition by siRNA during serum deprivation induces nuclear localization of the transcription factor forkhead box class O 1 (FOXO1), decreases nuclear phosphorylated-AKT (p-AKT), and p-FOXO1 protein expression, and increases phosphorylated-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK) protein expression. However, treatment with the AMPK inhibitor, compound C, reversed the reduction in the protein expression levels of nuclear p- AKT and p-FOXO1 and decreased the protein expression levels of p-AMPK and PEPCK in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA during serum deprivation.
Conclusion
These data show that SGLT2 mediates glucose uptake in hepatocytes and that SGLT2 inhibition during serum deprivation increases gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
- Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):568-577. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1770

- 1,545 View
- 113 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) has become an important tool for evaluating cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study evaluated the significance of CACS for future CVD through more than 10 years of follow-up in asymptomatic Korean populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) known to have a relatively low CACS burden.
Methods
We enrolled 981 asymptomatic T2DM patients without CVD at baseline who underwent CACS evaluation using multidetector computed tomography between January 2008 and December 2014. They were grouped into five predefined CACS categories based on Agatston scores and followed up by August 2020. The primary endpoint was incident CVD events, including coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial disease.
Results
The relative risk of CVD was significantly higher in patients with CACS ≥10, and the significance persisted after adjustment for known confounders. A higher CACS category indicated a higher incidence of future CVD: hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) 4.09 (1.79 to 9.36), 12.00 (5.61 to 25.69), and 38.79 (16.43 to 91.59) for 10≤ CACS <100, 100≤ CACS <400, and CACS ≥400, respectively. During the 12-year follow-up period, the difference in event-free survival more than doubled as the category increased. Patients with CACS below 10 had very low CVD incidence throughout the follow-up. The receiver operating characteristic analysis showed better area under curve when the CACS cutoff was 10 than 100.
Conclusion
CACS can be a sensitive marker of CVD risk. Specifically, CACS above 10 is an indicator of CVD high-risk requiring more intensive medical treatment in Koreans with T2DM.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):74-83. Published online February 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1293
- 4,882 View
- 235 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Dulaglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), has been shown to reduce body weight and liver fat content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Family with sequence similarity 3 member A (FAM3A) plays a vital role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. The aim of this study was to determine the mechanisms by which dulaglutide protects against hepatic steatosis in HepG2 cells treated with palmitic acid (PA).
Methods
HepG2 cells were pretreated with 400 μM PA for 24 hours, followed by treatment with or without 100 nM dulaglutide for 24 hours. Hepatic lipid accumulation was determined using Oil red O staining and triglyceride (TG) assay, and the expression of lipid metabolism-associated factor was analyzed using quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting.
Results
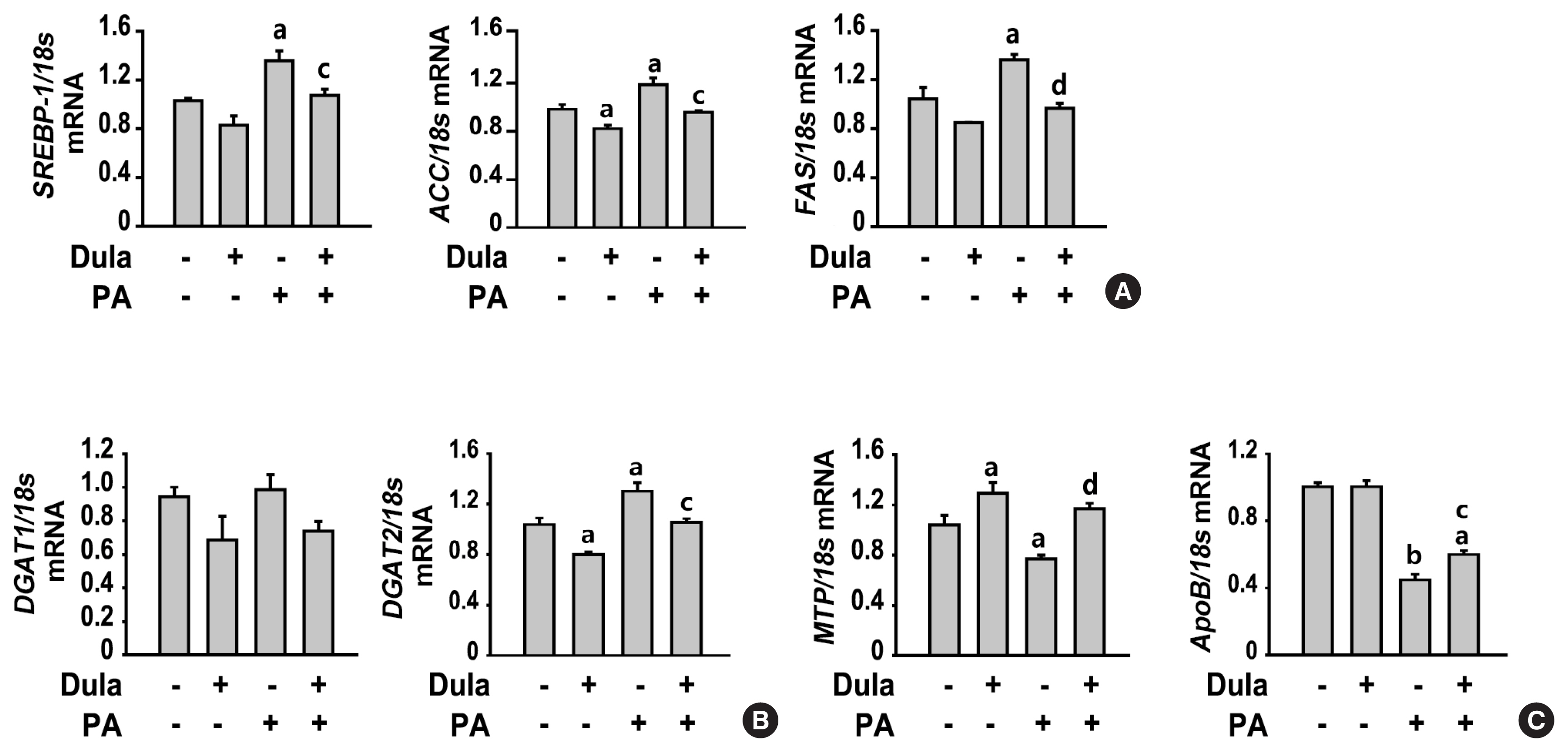
Dulaglutide significantly decreased hepatic lipid accumulation and reduced the expression of genes associated with lipid droplet binding proteins, de novo lipogenesis, and TG synthesis in PA-treated HepG2 cells. Dulaglutide also increased the expression of proteins associated with lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation and FAM3A in PA-treated cells. However, exendin-(9-39), a GLP-1R antagonist, reversed the expression of FAM3A, and fatty acid oxidation-associated factors increased due to dulaglutide. In addition, inhibition of FAM3A by siRNA attenuated the reducing effect of dulaglutide on TG content and its increasing effect on regulation of fatty acid oxidation.
Conclusion
These results suggest that dulaglutide could be used therapeutically for improving nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and its effect could be mediated in part via upregulation of FAM3A expression through a GLP-1R-dependent pathway. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- GLP-1/GLP-1RAs: New Options for the Drug Treatment of NAFLD
Haoran Jiang, Linquan Zang
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(2): 100. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Riccardo Nevola, Raffaella Epifani, Simona Imbriani, Giovanni Tortorella, Concetta Aprea, Raffaele Galiero, Luca Rinaldi, Raffaele Marfella, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1703. CrossRef - FAM3A mediates the phenotypic switch of human aortic smooth muscle cells stimulated with oxidised low-density lipoprotein by influencing the PI3K-AKT pathway
Lei Yang, Baoshun Du, Shitao Zhang, Maode Wang
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal.2023; 59(6): 431. CrossRef - ATP Secretion and Metabolism in Regulating Pancreatic Beta Cell Functions and Hepatic Glycolipid Metabolism
Jing Li, Han Yan, Rui Xiang, Weili Yang, Jingjing Ye, Ruili Yin, Jichun Yang, Yujing Chi
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH)
Xiaohan Xu, Kyle L. Poulsen, Lijuan Wu, Shan Liu, Tatsunori Miyata, Qiaoling Song, Qingda Wei, Chenyang Zhao, Chunhua Lin, Jinbo Yang
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- GLP-1/GLP-1RAs: New Options for the Drug Treatment of NAFLD

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Changes in Insulin Resistance Index and the Risk of Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Diabetes: Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
- Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Inha Jung, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1016-1028. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1110
- 4,149 View
- 128 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Fibrosis is the most important prognostic factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Insulin resistance plays a key role of fibrosis progression. We evaluated the association between changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) values and changes in fibrosis status in NAFLD.
Methods
We analyzed the data of 15,728 participants with NAFLD (86% men, mean age 40.5 years) who had no diabetes at baseline and visited our centers for health check-ups both in 2012 and 2016. The participants were classified into four groups according to the degree of change in HOMA-IR values from baseline to the end of follow-up: G1 (<0), G2 (0–0.50), G3 (0.51–1.00), and G4 (>1.00). NAFLD was assessed by ultrasonography, and fibrosis status was evaluated by the NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) and the aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI).
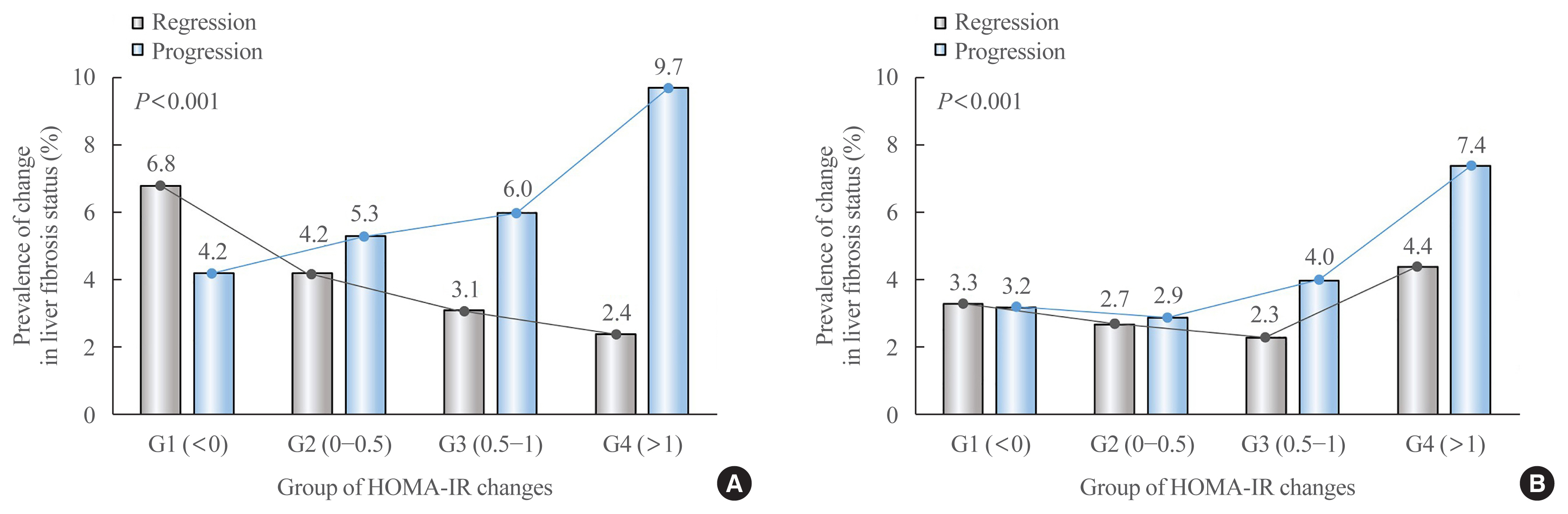
Results
After the 4-year follow-up, the multivariable-adjusted odds ratio (OR) for progression of fibrosis probability increased with increasing HOMA-IR values (OR, 2.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.87 to 2.71 for NFS; and OR, 2.55; 95% CI, 2.05 to 3.18 for APRI, G4). This tendency remained consistent throughout the subgroup analyses, except in those for female sex and a body mass index <25 kg/m2. The OR for regression of fibrosis probability decreased with increasing HOMA-IR values (OR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.43 for NFS, G4).
Conclusion
Changes in HOMA-IR values were associated with changes in fibrosis status in patients with NAFLD without diabetes, which underscores the role of insulin resistance in liver fibrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin Resistance/Sensitivity Measures as Screening Indicators of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Soodeh Jahangiri, Sohrab Nobarani, Azita Hekmatdoost, Marieh Salavatizadeh, Samira Soltanieh, Haleh Chehrehgosha, Hoda Taheri, Zeinab Montazeri, Fereshteh Attaran, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(4): 1430. CrossRef - Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: A 7-year retrospective cohort study of 3,496 adults using serial echocardiography
Gyuri Kim, Tae Yang Yu, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Cheol Bae, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; : 101534. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Yu Luo, Cuiyu Wang, Tian Zhang, Xiaoyu He, Jianan Hao, Andong Shen, Hang Zhao, Shuchun Chen, Luping Ren
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 293. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance Is Inversely Related to Incident Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Jun-Hyuk Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Kyongmin Park, Hye Sun Lee, Hoon-Ki Park, Jee Hye Han, Sang Bong Ahn
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3039. CrossRef - Machine learning models including insulin resistance indexes for predicting liver stiffness in United States population: Data from NHANES
Kexing Han, Kexuan Tan, Jiapei Shen, Yuting Gu, Zilong Wang, Jiayu He, Luyang Kang, Weijie Sun, Long Gao, Yufeng Gao
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The crosstalk between insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a culprit or a consequence?
Dae-Jeong Koo, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 132. CrossRef
- Insulin Resistance/Sensitivity Measures as Screening Indicators of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - The Effects of Glucose Lowering Agents on the Secondary Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):977-987. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1046
- 4,015 View
- 175 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
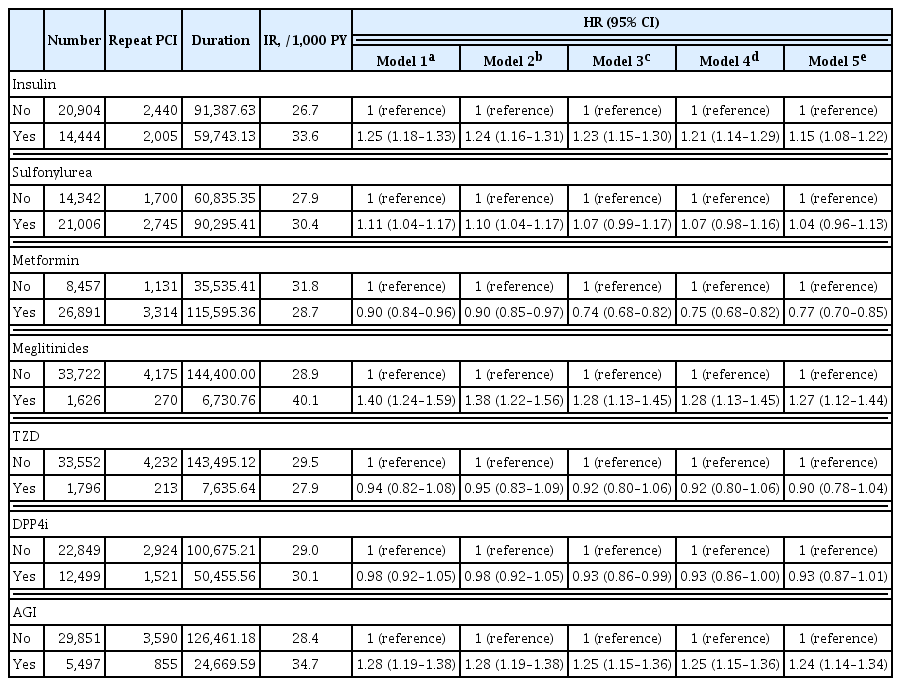
ePub - Background
Patients with diabetes have a higher risk of requiring repeated percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) than non-diabetic patients. We aimed to evaluate and compare the effects of anti-diabetic drugs on the secondary prevention of myocardial infarction among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
We analyzed the general health check-up dataset and claims data of the Korean National Health Insurance Service of 199,714 participants (age ≥30 years) who underwent PCIs between 2010 and 2013. Those who underwent additional PCI within 1 year of their first PCI (n=3,325) and those who died within 1 year (n=1,312) were excluded. Patients were classified according to their prescription records for glucose-lowering agents. The primary endpoint was the incidence rate of coronary revascularization.
Results
A total of 35,348 patients were included in the study. Metformin significantly decreased the risk of requiring repeat PCI in all patients (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.77). In obese patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥25 kg/m2, patients treated with thiazolidinedione (TZD) exhibited a decreased risk of requiring repeat revascularization than those who were not treated with TZD (aHR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.63 to 0.95). Patients treated with metformin showed a decreased risk of requiring revascularization regardless of their BMI. Insulin, meglitinide, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor were associated with increased risk of repeated PCI.
Conclusion
The risk of requiring repeat revascularization was lower in diabetic patients treated with metformin and in obese patients treated with TZD. These results suggest that physicians should choose appropriate glucose-lowering agents for the secondary prevention of coronary artery disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of systemic inflammation indices and lipid metabolism-related factors in coronary artery disease
Zhuoyan Zhao, Huan Lian, Yixiang Liu, Lixian Sun, Ying Zhang
Coronary Artery Disease.2023; 34(5): 306. CrossRef - Effect of metformin on adverse outcomes in T2DM patients: Systemic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Zhicheng Xu, Haidong Zhang, Chenghui Wu, Yuxiang Zheng, Jingzhou Jiang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment of a Predictive Model for Poor Prognosis of Incomplete Revascularization in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Multivessel Disease
Huan Lian, Zhuoyan Zhao, Kelin Ma, Zhenjiang Ding, Lixian Sun, Ying Zhang
Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis.2022; 28: 107602962211392. CrossRef
- Application of systemic inflammation indices and lipid metabolism-related factors in coronary artery disease

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Increased Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals with High Weight Variability
- Inha Jung, Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):845-854. Published online August 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1098
- 4,915 View
- 140 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
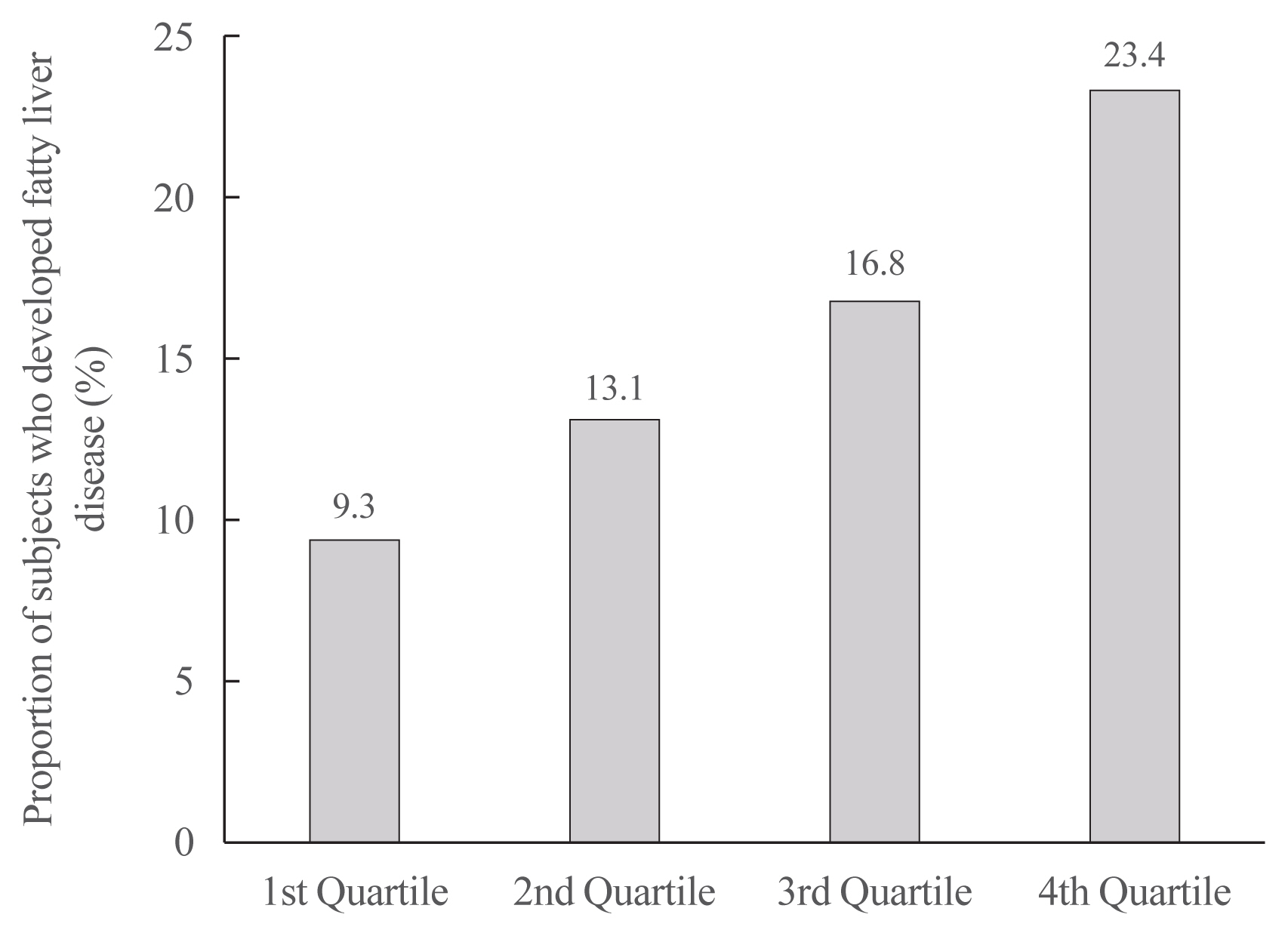
ePub - Background
Weight loss through lifestyle modification is recommended for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent studies have suggested that repeated loss and gain of weight is associated with worse health outcomes. This study aimed to examine the association between weight variability and the risk of NAFLD in patients without diabetes.
Methods
We examined the health-checkup data of 30,708 participants who had undergone serial examinations between 2010 and 2014. Weight variability was assessed using coefficient of variation and the average successive variability of weight (ASVW), which was defined as the sum of absolute weight changes between successive years over the 5-year period divided by 4. The participants were classified according to the baseline body mass index and weight difference over 4 years.
Results
On dividing the participants into four groups according to ASVW quartile groups, those in the highest quartile showed a significantly increased risk of NAFLD compared to those in the lowest quartile (odds ratio [OR], 1.89; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.63 to 2.19). Among participants without obesity at baseline, individuals with high ASVW showed increased risk of NAFLD (OR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.61 to 2.01). Participants with increased weight over 4 years and high ASVW demonstrated higher risk of NAFLD compared to those with stable weight and low ASVW (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 4.29 to 5.53).
Conclusion
Regardless of participant baseline obesity status, high weight variability was associated with an increased risk of developing NAFLD. Our results suggest that further effort is required to minimize weight fluctuations after achieving a desirable body weight. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in Macronutrients during Dieting Lead to Weight Cycling and Metabolic Complications in Mouse Model
Anouk Charlot, Anthony Bringolf, Léa Debrut, Joris Mallard, Anne-Laure Charles, Emilie Crouchet, Delphine Duteil, Bernard Geny, Joffrey Zoll
Nutrients.2024; 16(5): 646. CrossRef - Weight variability, physical functioning and incident disability in older adults
Katie J. McMenamin, Tamara B. Harris, Joshua F. Baker
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(4): 1648. CrossRef - Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 74. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease in individuals of normal weight
Mohammed Eslam, Hashem B. El-Serag, Sven Francque, Shiv K. Sarin, Lai Wei, Elisabetta Bugianesi, Jacob George
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2022; 19(10): 638. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Higher Weight Variability Could Bring You a Fatty Liver
Yeoree Yang, Jae-Hyoung Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 766. CrossRef - Autonomic Imbalance Increases the Risk for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Inha Jung, Da Young Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Hyemi Kwon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Won-Young Lee, Sung-Woo Park, Se Eun Park
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Changes in Macronutrients during Dieting Lead to Weight Cycling and Metabolic Complications in Mouse Model

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Non-Laboratory-Based Simple Screening Model for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Developed Using Multi-Center Cohorts
- Jiwon Kim, Minyoung Lee, Soo Yeon Kim, Ji-Hye Kim, Ji Sun Nam, Sung Wan Chun, Se Eun Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Joo Young Nam, Eun Seok Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):823-834. Published online August 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1074
- 4,434 View
- 137 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
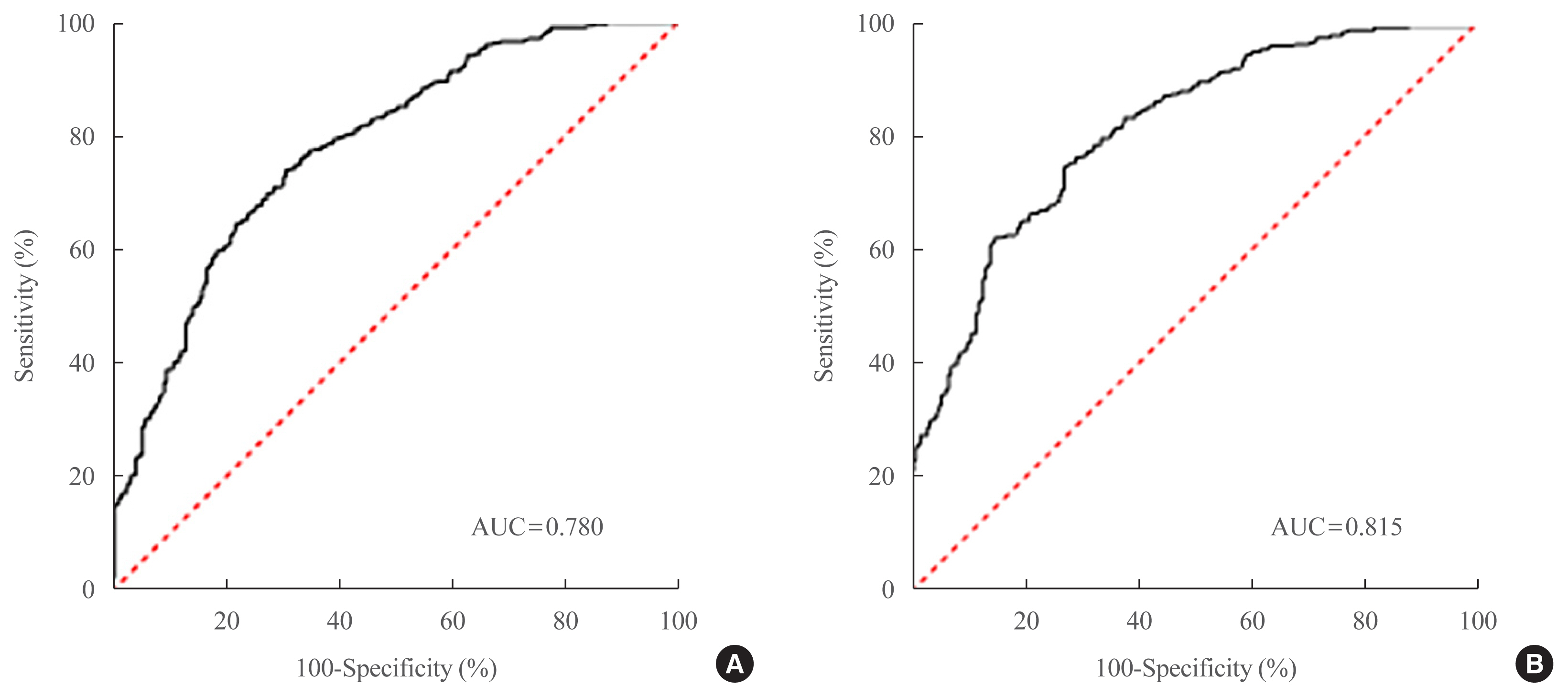
ePub - Background
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a risk factor that accelerates NAFLD progression, leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Thus, here we aimed to develop a simple model to predict the presence of NAFLD based on clinical parameters of patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 698 patients with T2DM who visited five medical centers were included. NAFLD was evaluated using transient elastography. Univariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify potential contributors to NAFLD, followed by multivariable logistic regression analyses to create the final prediction model for NAFLD.
Results
Two NAFLD prediction models were developed, with and without serum biomarker use. The non-laboratory model comprised six variables: age, sex, waist circumference, body mass index (BMI), dyslipidemia, and smoking status. For a cutoff value of ≥60, the prediction accuracy was 0.780 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.743 to 0.817). The second comprehensive model showed an improved discrimination ability of up to 0.815 (95% CI, 0.782 to 0.847) and comprised seven variables: age, sex, waist circumference, BMI, glycated hemoglobin, triglyceride, and alanine aminotransferase to aspartate aminotransferase ratio. Our non-laboratory model showed non-inferiority in the prediction of NAFLD versus previously established models, including serum parameters.
Conclusion
The new models are simple and user-friendly screening methods that can identify individuals with T2DM who are at high-risk for NAFLD. Additional studies are warranted to validate these new models as useful predictive tools for NAFLD in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—The Chicken or the Egg Dilemma
Marcin Kosmalski, Agnieszka Śliwińska, Józef Drzewoski
Biomedicines.2023; 11(4): 1097. CrossRef
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—The Chicken or the Egg Dilemma

- Endocrine Research
- Clusterin Protects Lipotoxicity-Induced Apoptosis via Upregulation of Autophagy in Insulin-Secreting Cells
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Min Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):943-953. Published online December 2, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.768
- 5,662 View
- 135 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
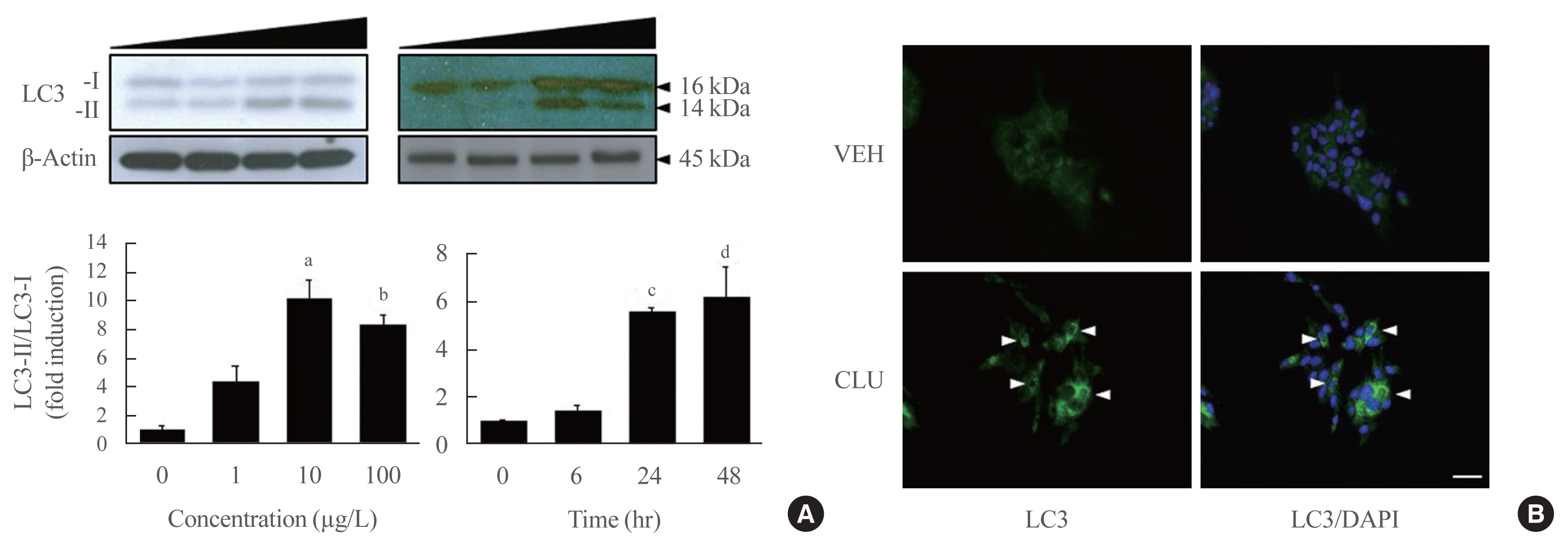
ePub - Background
There is a great need to discover factors that could protect pancreatic β-cells from apoptosis and thus prevent diabetes mellitus. Clusterin (CLU), a chaperone protein, plays an important role in cell protection in numerous cells and is involved in various cellular mechanisms, including autophagy. In the present study, we investigated the protective role of CLU through autophagy regulation in pancreatic β-cells.
Methods
To identify the protective role of CLU, mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells were incubated with CLU and/or free fatty acid (FFA) palmitate, and cellular apoptosis and autophagy were examined.
Results
Treatment with CLU remarkably upregulated microtubule-associated protein 1-light chain 3 (LC3)-II conversion in a doseand time-dependent manner with a significant increase in the autophagy-related 3 (Atg3) gene expression level, which is a mediator of LC3-II conversion. Moreover, co-immunoprecipitation and fluorescence microscopy experiments showed that the molecular interaction of LC3 with Atg3 and p62 was markedly increased by CLU. Stimulation of LC3-II conversion by CLU persisted in lipotoxic conditions, and FFA-induced apoptosis and dysfunction were simultaneously improved by CLU treatment. Finally, inhibition of LC3-II conversion by Atg3 gene knockdown markedly attenuated the cytoprotective effect of CLU.
Conclusion
Taken together, these findings suggest that CLU protects pancreatic β-cells against lipotoxicity-induced apoptosis via autophagy stimulation mediated by facilitating LC3-II conversion. Thus, CLU has therapeutic effects on FFA-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention to protect pancreatic beta cells in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Alexandra Coomans de Brachène, Corentin Scoubeau, Anyïshai E. Musuaya, Jose Maria Costa-Junior, Angela Castela, Julie Carpentier, Vitalie Faoro, Malgorzata Klass, Miriam Cnop, Decio L. Eizirik
Diabetologia.2023; 66(3): 450. CrossRef - Apolipoprotein J Attenuates Vascular Restenosis by Promoting Autophagy and Inhibiting the Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Ning Yang, Bo Dong, Yanqiu Song, Yang Li, Lu Kou, Qin Qin
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research.2022; 15(5): 1086. CrossRef - Targets for rescue from fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells
Seok-Woo Hong, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 57. CrossRef - Co-regulators of autophagy and the cell cycle in HFD − As treated mice
Marzieh Zeinvand-Lorestani, Mohammad Javad Khodayar, Ali Teimoori, Najmaldin Saki, Akram Ahangarpour, Ali Ranjbar, Hamed Zeinvand-Lorestani
Journal of Trace Elements and Minerals.2022; 2: 100018. CrossRef - Targeting pancreatic β cells for diabetes treatment
Chirag Jain, Ansarullah, Sara Bilekova, Heiko Lickert
Nature Metabolism.2022; 4(9): 1097. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Beta-Cell Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetes-Prone Situations and Potential Protection by GLP-1-Based Therapies
Safia Costes, Gyslaine Bertrand, Magalie A. Ravier
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(10): 5303. CrossRef
- Exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention to protect pancreatic beta cells in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes

- Clinical Study
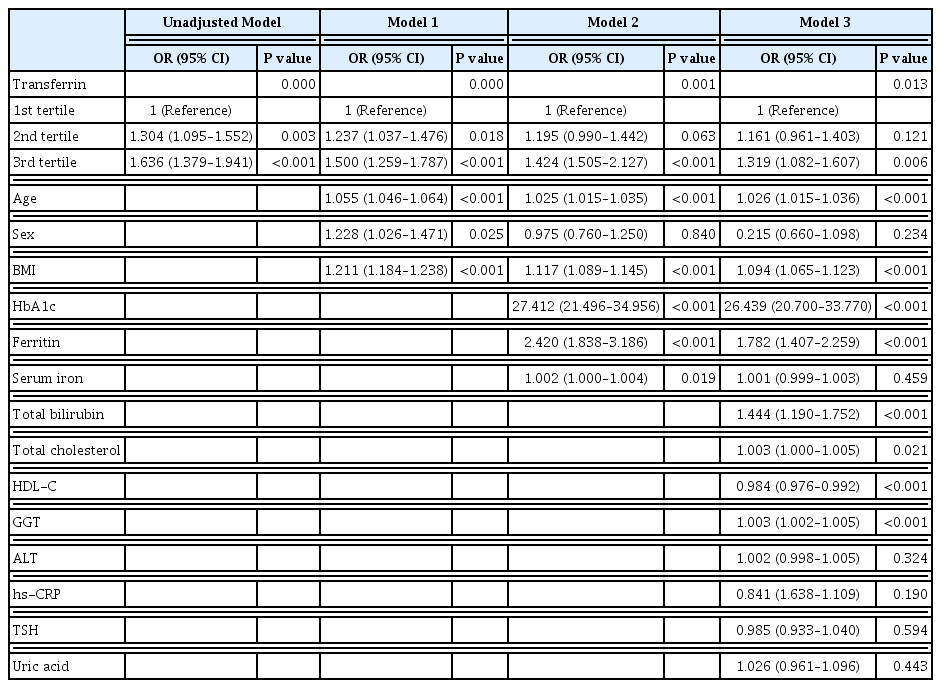
- Serum Transferrin Predicts New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Jong Dai Kim, Dong-Mee Lim, Keun-Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):610-617. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.721
- 4,393 View
- 98 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
It is well known that high serum ferritin, a marker of iron storage, predicts incident type 2 diabetes. Limited information is available on the association between transferrin, another marker of iron metabolism, and type 2 diabetes. Thus, we investigated the association between transferrin and incident type 2 diabetes.
Methods
Total 31,717 participants (mean age, 40.4±7.2 years) in a health screening program in 2005 were assessed via cross-sectional analysis. We included 30,699 subjects who underwent medical check-up in 2005 and 2009 and did not have type 2 diabetes at baseline in this retrospective longitudinal analysis.
Results
The serum transferrin level was higher in the type 2 diabetes group than in the non-type 2 diabetes group (58.32±7.74 μmol/L vs. 56.17±7.96 μmol/L, P<0.001). Transferrin correlated with fasting serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in the correlational analysis (r=0.062, P<0.001 and r=0.077, P<0.001, respectively) after full adjustment for covariates. Transferrin was more closely related to homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance than to homeostasis model assessment of β cell function (r=0.042, P<0.001 and r=–0.019, P=0.004, respectively) after full adjustment. Transferrin predicted incident type 2 diabetes in non-type 2 diabetic subjects in a multivariate linear regression analysis; the odds ratio (95% confidence interval [CI]) of the 3rd tertile compared to that in the 1st tertile of transferrin for incident diabetes was 1.319 (95% CI, 1.082 to 1.607) after full adjustment (P=0.006).
Conclusion
Transferrin is positively associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes
Xingyue Wang, You Wang, Junjie Hou, Hongyang Liu, Rong Zeng, Xiangyu Li, Mei Han, Qingrun Li, Linong Ji, Desi Pan, Weiping Jia, Wen Zhong, Tao Xu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Proteomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer in Patients with Diabetes
Muhammad Mujammami, Mohamed Rafiullah, Khalid Akkour, Assim A. Alfadda, Afshan Masood, Salini Scaria Joy, Hani Alhalal, Maria Arafah, Eman Alshehri, Ibrahim O. Alanazi, Hicham Benabdelkamel
ACS Omega.2024; 9(4): 4721. CrossRef - Association between systemic iron status and β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Yao Qin, Yiting Huang, Yuxiao Li, Lu Qin, Qianying Wei, Xin Chen, Chuanhui Yang, Mei Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Serum Level of Ceruloplasmin, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Transferrin as Markers of Severity in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Patricia-Andrada Reștea, Ștefan Țigan, Laura Grațiela Vicaș, Luminița Fritea, Eleonora Marian, Tunde Jurca, Annamaria Pallag, Iulius Liviu Mureșan, Corina Moisa, Otilia Micle, Mariana Eugenia Mureșan
Microbiology Research.2023; 14(4): 1670. CrossRef
- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes

- Clinical Study
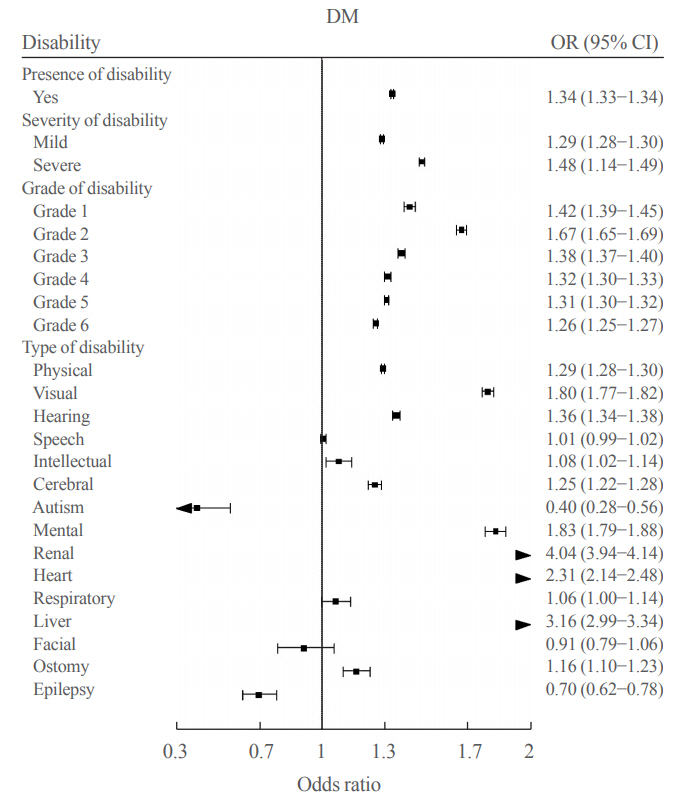
- The Prevalence and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults with Disabilities in Korea
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):552-561. Published online July 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.653
- 8,100 View
- 188 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
People with disabilities are at risk of secondary conditions such as diabetes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and risk of type 2 diabetes in South Korea, especially among people with all types of disabilities.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service, with two disabilityfree controls matched for each participant with disabilities by age and sex. Information regarding the type, severity and grade of disabilities was obtained based on the National Disability Registry. Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes was defined according to the following criteria: presence of International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification codes E11, E12, E13, or E14 and claims for at least one oral anti-diabetic agent or insulin at baseline, or fasting glucose level ≥126 mg/dL.
Results
We included 1,297,806 participants with disabilities and 2,943,719 control. Out of 4,241,525 participants, 841,990 (19.9%) were diagnosed with diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes was higher in the disability group compared with individuals without disabilities (23.1% vs. 18.4%). The odds of having diabetes was higher in the disability group compared with the control group (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.33 to 1.34). The results showed higher prevalence of diabetes in the mildly disabled group (23.2%) than in the severely disabled group (22.7%).
Conclusion
The prevalence and risk of diabetes were higher in people with disabilities compared with the general population. Physicians and public health authorities should focus on people with disabilities for proper diabetes management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - Bipolar disorder and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, heart failure, and all-cause mortality: a population-based matched cohort study in South Korea
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychotic Disorders and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases, and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Matched Cohort Study
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 122. CrossRef - Pathways linking health literacy to self-care in diabetic patients with physical disabilities: A moderated mediation model
Hye Jin Nam, Ju Young Yoon, Wen-Jun Tu
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(3): e0299971. CrossRef - Dysphagia Requiring Medical Attention in Parkinson’s Disease: A Korean Population-Based Study
Seungwoo Cha, Won Kee Chang, Hee-Mun Cho, Kyungdo Han, Nam-Jong Paik, Sohyun Kwon, Won-Seok Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Disparities in diabetes-related avoidable hospitalization among diabetes patients with disability using a nationwide cohort study
Hin Moi Youn, Dong-Woo Choi, Sung-In Jang, Eun-Cheol Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Disability type–specific mortality patterns and life expectancy among disabled people in South Korea using 10-year combined data between 2008 and 2017
Jinwook Bahk, Hee-Yeon Kang, Young-Ho Khang
Preventive Medicine Reports.2022; 29: 101958. CrossRef - Cholecystectomy reduces the risk of myocardial and cerebral infarction in patients with gallstone-related infection
Seon Mee Park, Hyun Jung Kim, Tae Uk Kang, Heather Swan, Hyeong Sik Ahn
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nationwide trends in the incidence of tuberculosis among people with disabilities in Korea:
a nationwide serial cross-sectional study
Jinsoo Min, So Young Kim, Jong Eun Park, Yeon Yong Kim, Jong Hyock Park
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022098. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and future risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eun Sil Koh, Oak-Kee Hong, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108799. CrossRef - Diabetes in People with Disabilities: a Call for Action
Inha Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(4): 82. CrossRef
- Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea

- Clinical Study
- Serum Adiponectin and Progranulin Level in Patients with Benign Thyroid Nodule or Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Ji-Sup Yun, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):396-406. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.396

- 5,637 View
- 108 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity is associated with thyroid cancer risk. Adiponectin has insulin-sensitizing and anti-inflammatory effects, while progranulin is associated with inflammation and tumorigenesis. We investigated serum adiponectin and progranulin levels in patients with benign thyroid nodule (benign group) and papillary thyroid cancer (PTC; PTC group). The associations between these levels and the clinicopathological features of PTC were evaluated.
Methods
We included 157 patients who underwent thyroid surgery (17% of benign and 83% of PTC group). Clinicopathological features including size, lymph node metastasis, extrathyroidal extension (ETE), multifocality, American Thyroid Association risk stratification were evaluated.
Results
The age was 42.0 years, and 69% were female. Serum adiponectin and progranulin levels were 6.3 μg/mL and 101.5 ng/mL in the benign group and 5.4 μg/mL and 106.1 ng/mL in the PTC group, respectively (P=0.6 and P=0.4, respectively). Serum adiponectin levels showed no significant differences according to clinicopathological features of PTC. The proportions of patients with primary tumor size >1 cm were 3%, 5%, 8%, and 8% according to serum progranulin level quartiles, respectively (P=0.03). The proportions of patients with microscopic/gross ETE were 8%/0%, 9%/1%, 11%/1%, and 11%/2% according to serum progranulin level quartiles, respectively. Median serum progranulin level was significantly higher in patients with PTC >1 cm than in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (P=0.04, 115.3 ng/mL and 104.7 ng/mL, respectively).
Conclusion
Serum adiponectin and progranulin levels showed no significant difference between benign and PTC groups. Increased serum progranulin levels were significantly associated with PTC >1 cm and microscopic and gross ETE. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the logic and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of AdipoRon-based adiponectin replacement therapy against hormone-related cancers—a systematic review
Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Andreline Franchi Sosin, Caroline Barbalho Lamas, Ricardo de Alvares Goulart, Jesselina Francisco dos Santos Haber, Claudia Rucco Penteado Detregiachi, Sandra Maria Barbalho
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024; 397(4): 2067. CrossRef - Adiponectin Inhibits the Progression of Obesity-Associated Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Autophagy
Changlin Li, Jiao Zhang, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Nan Liang, Haixia Guan, Hui Sun
Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Progranulin Oncogenic Network in Solid Tumors
Elisa Ventura, Giacomo Ducci, Reyes Benot Dominguez, Valentina Ruggiero, Antonino Belfiore, Elena Sacco, Marco Vanoni, Renato V. Iozzo, Antonio Giordano, Andrea Morrione
Cancers.2023; 15(6): 1706. CrossRef - Obesity and thyroid cancer risk
Lauren C. Burrage, Donald S.A. McLeod, Susan J. Jordan
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2023; 30(5): 244. CrossRef - Progranulin promoted the proliferation, metastasis, and suppressed apoptosis via JAK2-STAT3/4 signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yanxu Dong, Hao Tan, Lidong Wang, Zhen Liu
Cancer Cell International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: An Update
Fabiana Franchini, Giuseppe Palatucci, Annamaria Colao, Paola Ungaro, Paolo Emidio Macchia, Immacolata Cristina Nettore
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(3): 1116. CrossRef - Obesity and Overweight Are Associated with Minimal Extrathyroidal Extension, Multifocality and Bilaterality of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Krzysztof Kaliszewski, Dorota Diakowska, Marta Rzeszutko, Jerzy Rudnicki
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(5): 970. CrossRef - Adiponectin and Thyroid Cancer: Insight into the Association between Adiponectin and Obesity
Yuanyuan Zhou, Ying Yang, Taicheng Zhou, Bai Li, Zhanjian Wang
Aging and disease.2021; 12(2): 597. CrossRef
- Exploring the logic and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of AdipoRon-based adiponectin replacement therapy against hormone-related cancers—a systematic review

- Endocrine Research
- Deficiency of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Reduces the Expression of Prohibitin and Causes β-Cell Impairment via Mitochondrial Dysregulation
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):403-412. Published online September 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.403
- 4,204 View
- 50 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Emerging evidence suggests that sphingolipids may be involved in type 2 diabetes. However, the exact signaling defect through which disordered sphingolipid metabolism induces β-cell dysfunction remains unknown. The current study demonstrated that sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), the product of sphingosine kinase (SphK), is an essential factor for maintaining β-cell function and survival via regulation of mitochondrial action, as mediated by prohibitin (PHB).
Methods We examined β-cell function and viability, as measured by mitochondrial function, in mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells in response to manipulation of cellular S1P and PHB levels.
Results Lack of S1P induced by sphingosine kinase inhibitor (SphKi) treatment caused β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis, with repression of mitochondrial function shown by decreases in cellular adenosine triphosphate content, the oxygen consumption rate, the expression of oxidative phosphorylation complexes, the mitochondrial membrane potential, and the expression of key regulators of mitochondrial dynamics (mitochondrial dynamin-like GTPase [OPA1] and mitofusin 1 [MFN1]). Supplementation of S1P led to the recovery of mitochondrial function and greatly improved β-cell function and viability. Knockdown of SphK2 using small interfering RNA induced mitochondrial dysfunction, decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS), and reduced the expression of PHB, an essential regulator of mitochondrial metabolism. PHB deficiency significantly reduced GSIS and induced mitochondrial dysfunction, and co-treatment with S1P did not reverse these trends.
Conclusion Altogether, these data suggest that S1P is an essential factor in the maintenance of β-cell function and survival through its regulation of mitochondrial action and PHB expression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial Cristae Morphology Reflecting Metabolism, Superoxide Formation, Redox Homeostasis, and Pathology
Petr Ježek, Martin Jabůrek, Blanka Holendová, Hana Engstová, Andrea Dlasková
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2023; 39(10-12): 635. CrossRef - Sphingolipids in mitochondria—from function to disease
Maryam Jamil, Lauren Ashley Cowart
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine‐1‐phosphate in mitochondrial function and metabolic diseases
Meng Duan, Pan Gao, Sheng‐xi Chen, Petr Novák, Kai Yin, Xiao Zhu
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Involvement of miR‐27a‐3p in diabetic nephropathy via affecting renal fibrosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Lina Wu, Qingzhu Wang, Feng Guo, Xiaojun Ma, Jiao Wang, Yanyan Zhao, Yushan Yan, Guijun Qin
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2021; 236(2): 1454. CrossRef - Sphingosine‐1‐phosphate in acute exercise and training
Katarzyna Hodun, Adrian Chabowski, Marcin Baranowski
Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports.2021; 31(5): 945. CrossRef - The Ethyl Acetate Extract From Celastrus orbiculatus Promotes Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Mitochondria Regulation by PHB
Lide Tao, Zixin Yin, Tengyang Ni, Zewen Chu, Shihua Hao, Zeyu Wang, Masataka Sunagawa, Haibo Wang, Yanqing Liu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine 1-phosphate Stimulates Insulin Secretion and Improves Cell Survival by Blocking Voltage-dependent K+ Channels in β Cells
Zhihong Liu, Huanhuan Yang, Linping Zhi, Huan Xue, Zhihong Lu, Yanli Zhao, Lijuan Cui, Tao Liu, Shouan Ren, Peifeng He, Yunfeng Liu, Yi Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine-1 Phosphate Lyase Regulates Sensitivity of Pancreatic Beta-Cells to Lipotoxicity
Yadi Tang, Thomas Plötz, Markus H. Gräler, Ewa Gurgul-Convey
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10893. CrossRef - Sphingolipids and Mitochondrial Dynamic
Lais Brigliadori Fugio, Fernanda B. Coeli-Lacchini, Andréia Machado Leopoldino
Cells.2020; 9(3): 581. CrossRef - Diminished Sphingolipid Metabolism, a Hallmark of Future Type 2 Diabetes Pathogenesis, Is Linked to Pancreatic β Cell Dysfunction
Saifur R. Khan, Yousef Manialawy, Andreea Obersterescu, Brian J. Cox, Erica P. Gunderson, Michael B. Wheeler
iScience.2020; 23(10): 101566. CrossRef - Neuronal Metabolism and Neuroprotection: Neuroprotective Effect of Fingolimod on Menadione-Induced Mitochondrial Damage
Antonio Gil, Elisa Martín-Montañez, Nadia Valverde, Estrella Lara, Federica Boraldi, Silvia Claros, Silvana-Yanina Romero-Zerbo, Oscar Fernández, Jose Pavia, Maria Garcia-Fernandez
Cells.2020; 10(1): 34. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Ceramide and Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in adipose dysfunction
Zijian Fang, Susan Pyne, Nigel J. Pyne
Progress in Lipid Research.2019; : 100991. CrossRef - Dynamic of mitochondrial network, cristae, and mitochondrial nucleoids in pancreatic β-cells
Petr Ježek, Andrea Dlasková
Mitochondrion.2019; 49: 245. CrossRef - Sphingosine kinase 1 overexpression induces MFN2 fragmentation and alters mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ handling in HeLa cells
I. Pulli, C. Löf, T. Blom, M.Y. Asghar, T. Lassila, N. Bäck, K.-L. Lin, J.H. Nyström, K. Kemppainen, D.M. Toivola, E. Dufour, A. Sanz, H.M. Cooper, J.B. Parys, K. Törnquist
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2019; 1866(9): 1475. CrossRef - Ceramide and sphingosine 1-phosphate in adipose dysfunction
Zijian Fang, Susan Pyne, Nigel J. Pyne
Progress in Lipid Research.2019; 74: 145. CrossRef - S1P/S1P Receptor Signaling in Neuromuscolar Disorders
Elisabetta Meacci, Mercedes Garcia-Gil
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(24): 6364. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial Cristae Morphology Reflecting Metabolism, Superoxide Formation, Redox Homeostasis, and Pathology

- Thyroid
- Prevalence and Annual Incidence of Thyroid Disease in Korea from 2006 to 2015: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Hyemi Kwon, Jin-hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Ji Min Han, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):260-267. Published online June 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.260
- 6,406 View
- 128 Download
- 37 Web of Science
- 37 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The incidence of thyroid nodules has increased worldwide in recent years. Thyroid dysfunction is a potential risk factor for hypercholesterolemia, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, arrhythmia, and neuropsychiatric disease. This study investigated the prevalence and annual incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism in Koreans.
Methods In this nationwide population-based cohort study, 51,834,660 subjects were included using the National Health Information database from 2006 to 2015, after the exclusion of subjects with thyroid cancer.
Results The prevalence in Korea in 2015 of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism in patients taking thyroid hormone, and hyperthyroidism in patients undergoing treatment was 15.82/1,000 population, 15.94/1,000 population, and 2.76/1,000 population, respectively. All these diseases were more prevalent among women than among men. The number of incident cases of these three thyroid diseases steadily increased from 2006 to 2012, and then decreased through 2015. The incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism treated with thyroid hormone, and treated hyperthyroidism was 6.79/1,000 population, 1.76/1,000 population, and 0.55/1,000 population, respectively, in Korea in 2015. The use of methimazole continuously increased, from 33% of total antithyroid drug prescriptions in 2006 to 74.4% in 2015, and it became the most frequently prescribed antithyroid drug in Korea. In contrast, the use of propylthiouracil continuously decreased.
Conclusion This was the first nationwide study of the prevalence and annual incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism to take into account recent changes and to include the current status of patients receiving treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- New-onset atrial fibrillation in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: association with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs treatment
Hyung Woo Kim, Minkyung Han, Inkyung Jung, Sung Soo Ahn
Rheumatology.2024; 63(3): 630. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer Among Young Adults in South Korea
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Sun Joon Moon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1095. CrossRef - Endocrine and metabolic comorbidities in primary cicatricial alopecia: A nationwide population‐based study
Da‐Ae Yu, Seong Rae Kim, Soo Ick Cho, Ohsang Kwon
The Journal of Dermatology.2024; 51(3): 429. CrossRef - Risk of non-thyroidal autoimmune diseases in patients with Graves’ disease: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Seo Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Ji-Won Kwon, Ji-Min Kweon, Ju-Yeun Lee
Rheumatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Risk in Graves Disease with Radioactive131I Treatment: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Kyoung Jin Kim, Eyun Song, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim
Journal of Nuclear Medicine.2024; : jnumed.123.266531. CrossRef - Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients
Jung-Chi Hsu, Kang-Chih Fan, Ting-Chuan Wang, Shu-Lin Chuang, Ying-Ting Chao, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Lian-Yu Lin, Lung-Chun Lin
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Myotonic dystrophy type 1 in South Korea: a comprehensive analysis of cancer and comorbidity risks
Incheol Seo, Jin-Mo Park
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of ITM2A rs1751094 polymorphism on X chromosome in Korean pediatric patients with autoimmune thyroid disease
Won K. Cho, In‐Cheol Baek, Sung E. Kim, Mirae Kim, Tai‐Gyu Kim, Byung‐Kyu Suh
Immunity, Inflammation and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Risk Stratification of Follicular-patterned Thyroid Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy by Histologic Subtyping and RAS Variant-specific Immunohistochemistry
Meejeong Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(2): 247. CrossRef - Cancer and Mortality Risks of Graves’ Disease in South Korea Based on National Data from 2010 to 2019
Young Ju Choi, Kyungdo Han, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Byung-Kyu Suh
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 535. CrossRef - Acromegaly and the long-term fracture risk of the vertebra and hip: a national cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Bong-Sung Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(9): 1591. CrossRef - Association of Thyroid Hormone Medication Adherence With Risk of Dementia
Saemi Han, Seogsong Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Sun Jae Park, Kyae Hyung Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Yoosun Cho, Joung Sik Son, Sang Min Park
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e225. CrossRef - Increased risk of incident gout in patients with hyperthyroidism: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Ju-Yeun Lee, So-Yeon Park, Seo Young Sohn
Rheumatology International.2023; 44(3): 451. CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 436. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of chemokine gene polymorphisms in Korean children with autoimmune thyroid disease
Chungwoo Shin, In-Cheol Baek, Won Kyoung Cho, Tai-Gyu Kim, Byung-Kyu Suh
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the status of treatment of benign thyroid diseases — a public health problem aggravated in the COVID-19 pandemic era
Giulianno Molina Melo, Antonio José Gonçalves, Fernando Walder, Carolina Ferraz, Murilo Catafesta Neves, Marcio Abrahão, Onivaldo Cervantes
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2022; 88(6): 982. CrossRef - Graves’ disease and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: a Korean population-based study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Jinyoung Youn, Ji Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Brain Communications.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Graves’ Disease and the Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Korean Population-Based Study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Hye Ryoun Jang, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 281. CrossRef - Incidence of hypothyroidism after treatment for breast cancer: A Korean population-based study
Jongmoo Park, Choongrak Kim, Yongkan Ki, Wontaek Kim, Jiho Nam, Donghyun Kim, Dahl Park, Hosang Jeon, Dong Woon Kim, Ji Hyeon Joo, Claudio Andaloro
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269893. CrossRef - Genome-wide association study of hyperthyroidism based on electronic medical record from Taiwan
Ting-Yuan Liu, Wen-Ling Liao, Tzu-Yuan Wang, Chia-Jung Chan, Jan-Gowth Chang, Yu-Chia Chen, Hsing-Fang Lu, Hsien-Hui Yang, Shih-Yin Chen, Fuu-Jen Tsai
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Graves’ disease, its treatments, and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A Korean population-based study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dughyun Choi, Chul-Hee Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Jee Soo Kim, Seung-Jung Park, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of autoimmune diseases in recurrent aphthous ulcer patients: A nationwide population study
Young Chan Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Young‐Gyu Eun, Ran Song, In‐Hwan Oh
Oral Diseases.2021; 27(6): 1443. CrossRef - Hyperthyroidism Prevalence in China After Universal Salt Iodization
Chuyuan Wang, Yongze Li, Di Teng, Xiaoguang Shi, Jianming Ba, Bing Chen, Jianling Du, Lanjie He, Xiaoyang Lai, Yanbo Li, Haiyi Chi, Eryuan Liao, Chao Liu, Libin Liu, Guijun Qin, Yingfen Qin, Huibiao Quan, Bingyin Shi, Hui Sun, Xulei Tang, Nanwei Tong, Gui
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comorbidity network analysis related to obesity in middle-aged and older adults: findings from Korean population-based survey data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021018. CrossRef - Prevalence of Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism and its Correlation with Serum Antithyroglobulin among patients in Kirkuk-Iraq
Sabah Mohammed Salih, Wijdan Abdullameer Kamel, Mohammed Talat Abbas, Kasim Sakran Abass
Journal Of Advanced Pharmacy Education And Research.2021; 11(2): 57. CrossRef - A nationwide study of patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance with a 10-year follow-up in South Korea
Ka-Won Kang, Ji Eun Song, Byung-Hyun Lee, Min Ji Jeon, Eun Sang Yu, Dae Sik Kim, Se Ryeon Lee, Hwa Jung Sung, Chul Won Choi, Yong Park, Byung Soo Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and Mortality of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke in Patients with Hyperthyroidism: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea
Hyun Jung Kim, Taeuk Kang, Min Ji Kang, Hyeong Sik Ahn, Seo Young Sohn
Thyroid.2020; 30(7): 955. CrossRef - Vitamin D supplementation does not prevent the recurrence of Graves’ disease
Yoon Young Cho, Yun Jae Chung
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Binding and Activity of Tetrabromobisphenol A Mono-Ether Structural Analogs to Thyroid Hormone Transport Proteins and Receptors
Xiao-Min Ren, Linlin Yao, Qiao Xue, Jianbo Shi, Qinghua Zhang, Pu Wang, Jianjie Fu, Aiqian Zhang, Guangbo Qu, Guibin Jiang
Environmental Health Perspectives.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome and its components in Chinese patients with a range of thyroid-stimulating hormone concentrations
Kun Tang, Qiao Zhang, Nian-chun Peng, Miao Zhang, Shu-jing Xu, Hong Li, Ying Hu, Chun-ju Xue, Li-xin Shi
Journal of International Medical Research.2020; 48(11): 030006052096687. CrossRef - The Association of Overt and Subclinical Hyperthyroidism with the Risk of Cardiovascular Events and Cardiovascular Mortality: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Cohort Studies
Seo Young Sohn, Eunyoung Lee, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 786. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Disease in Patients Surgically Treated for Pituitary Disease
Kim, Cho, Ku, Jung, Moon, Kim, Shin, Kim, Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(8): 1142. CrossRef - Association of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Hormones with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Euthyroid Children and Adolescents Aged 10–18 Years: A Population-Based Study
Cheol Gyu Ma, Young Suk Shim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight change is significantly associated with risk of thyroid cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Cheol-Young Park
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the relationship of subclinical hypothyroidism with metabolic syndrome and its components in adolescents: a population-based study
Min-Kyung Lee, Yoo Mee Kim, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Young Jun Won, Se Hwa Kim
Endocrine.2019; 65(3): 608. CrossRef - Autoimmune thyroiditis and central serous chorioretinopathy may have a relation
Brijesh Takkar, Harsha Saxena, Anubha Rathi, Rekha Singh
Medical Hypotheses.2018; 121: 180. CrossRef
- New-onset atrial fibrillation in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: association with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs treatment

- Diabetes
- Pioglitazone Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Inflammation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pancreatic β-Cells
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):105-113. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.105
- 6,244 View
- 96 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activator gamma (PPARγ) is a useful therapeutic target for obesity and diabetes, but its role in protecting β-cell function and viability is unclear.
Methods To identify the potential functions of PPARγ in β-cells, we treated mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells with the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone in conditions of lipotoxicity, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and inflammation.
Results Palmitate-treated cells incubated with pioglitazone exhibited significant improvements in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and the repression of apoptosis, as shown by decreased caspase-3 cleavage and poly (adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose) polymerase activity. Pioglitazone also reversed the palmitate-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 6 [IL-6], and IL-1β) and ER stress markers (phosphor-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α, glucose-regulated protein 78 [GRP78], cleaved-activating transcription factor 6 [ATF6], and C/EBP homologous protein [CHOP]), and pioglitazone significantly attenuated inflammation and ER stress in lipopolysaccharide- or tunicamycin-treated MIN6 cells. The protective effect of pioglitazone was also tested in pancreatic islets from high-fat-fed KK-Ay mice administered 0.02% (wt/wt) pioglitazone or vehicle for 6 weeks. Pioglitazone remarkably reduced the expression of ATF6α, GRP78, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, prevented α-cell infiltration into the pancreatic islets, and upregulated glucose transporter 2 (Glut2) expression in β-cells. Moreover, the preservation of β-cells by pioglitazone was accompanied by a significant reduction of blood glucose levels.
Conclusion Altogether, these results support the proposal that PPARγ agonists not only suppress insulin resistance, but also prevent β-cell impairment via protection against ER stress and inflammation. The activation of PPARγ might be a new therapeutic approach for improving β-cell survival and insulin secretion in patients with diabetes mellitus
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nr1h4 and Thrb ameliorate ER stress and provide protection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s
Nancy Ahuja, Shalini Gupta, Rashmi Arora, Ella Bhagyaraj, Drishti Tiwari, Sumit Kumar, Pawan Gupta
Life Science Alliance.2024; 7(7): e202302416. CrossRef - Prosthetic vascular grafts engineered to combat calcification: Progress and future directions
Taylor K. Brown, Sara Alharbi, Karen J. Ho, Bin Jiang
Biotechnology and Bioengineering.2023; 120(4): 953. CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes mellitus, and cardiometabolic risk: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2023
Harold Edward Bays, Shagun Bindlish, Tiffany Lowe Clayton
Obesity Pillars.2023; 5: 100056. CrossRef - Metformin promotes osteogenic differentiation and prevents hyperglycaemia-induced osteoporosis by suppressing PPARγ expression
Lifeng Zheng, Ximei Shen, Yun Xie, Hong Lian, Sunjie Yan, Shizhong Wang
Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.2023; 55(3): 394. CrossRef - Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors as targets to treat metabolic diseases: Focus on the adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas
Henrique Souza-Tavares, Carolline Santos Miranda, Isabela Macedo Lopes Vasques-Monteiro, Cristian Sandoval, Daiana Araujo Santana-Oliveira, Flavia Maria Silva-Veiga, Aline Fernandes-da-Silva, Vanessa Souza-Mello
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 29(26): 4136. CrossRef - Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase upregulation contributes to palmitate-elicited peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor transactivation in hepatocytes
Qing Song, Jun Wang, Alexandra Griffiths, Samuel Man Lee, Iredia D. Iyamu, Rong Huang, Jose Cordoba-Chacon, Zhenyuan Song
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2023; 325(1): C29. CrossRef - The global perspective on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in ectopic fat deposition: A review
Yanhao Qiu, Mailin Gan, Xingyu Wang, Tianci Liao, Qiuyang Chen, Yuhang Lei, Lei Chen, Jinyong Wang, Ye Zhao, Lili Niu, Yan Wang, Shunhua Zhang, Li Zhu, Linyuan Shen
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 253: 127042. CrossRef - Chemical inducer of regucalcin attenuates lipopolysaccharide‐induced inflammatory responses in pancreatic MIN6 β‐cells and RAW264.7 macrophages
Tomiyasu Murata, Kazunori Hashimoto, Susumu Kohno, Chiaki Takahashi, Masayoshi Yamaguchi, Chihiro Ito, Itoigawa Masataka, Roji Kojima, Kiyomi Hikita, Norio Kaneda
FEBS Open Bio.2022; 12(1): 175. CrossRef - Targets for rescue from fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells
Seok-Woo Hong, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 57. CrossRef - Analysis of changes in the proteomic profile of porcine corpus luteum during different stages of the oestrous cycle: effects of PPAR gamma ligands
Zuzanna Kunicka, Karol Mierzejewski, Aleksandra Kurzyńska, Robert Stryiński, Jesús Mateos, Mónica Carrera, Monika Golubska, Iwona Bogacka, Xiaolong Wang
Reproduction, Fertility and Development.2022; 34(11): 776. CrossRef - Activation of PPARγ Protects Obese Mice from Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Yin Tang, Ke Wei, Ling Liu, Jingyue Ma, Siqi Wu, Wenjing Tang, Stéphane Mandard
PPAR Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Pioglitazone on endoplasmic reticulum stress regarding in situ perfusion rat model
Vivien Telek, Luca Erlitz, Ibitamuno Caleb, Tibor Nagy, Mónika Vecsernyés, Bálint Balogh, György Sétáló, Péter Hardi, Gábor Jancsó, Ildikó Takács
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2021; 79(2): 311. CrossRef - Inflammation in Metabolic Diseases and Insulin Resistance
Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(2): 31. CrossRef - Current Status of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Type II Diabetes
Sagir Mustapha, Mustapha Mohammed, Ahmad Khusairi Azemi, Abubakar Ibrahim Jatau, Aishatu Shehu, Lukman Mustapha, Ibrahim Muazzamu Aliyu, Rabi’u Nuhu Danraka, Abdulbasit Amin, Auwal Adam Bala, Wan Amir Nizam Wan Ahmad, Aida Hanum Ghulam Rasool, Mohd Rais M
Molecules.2021; 26(14): 4362. CrossRef - JunD Regulates Pancreatic β-Cells Function by Altering Lipid Accumulation
Kexin Wang, Yixin Cui, Peng Lin, Zhina Yao, Yu Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pioglitazone even at low dosage improves NAFLD in type 2 diabetes: clinical and pathophysiological insights from a subgroup of the TOSCA.IT randomised trial
Giuseppe Della Pepa, Marco Russo, Marilena Vitale, Fabrizia Carli, Claudia Vetrani, Maria Masulli, Gabriele Riccardi, Olga Vaccaro, Amalia Gastaldelli, Angela A. Rivellese, Lutgarda Bozzetto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108984. CrossRef - Radioprotective Effect of Pioglitazone Against Genotoxicity Induced by Ionizing Radiation in Healthy Human Lymphocytes
Roya Kazemi, Seyed J. Hosseinimehr
Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry .2021; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Recent Insights Into Mechanisms of β-Cell Lipo- and Glucolipotoxicity in Type 2 Diabetes
Maria Lytrivi, Anne-Laure Castell, Vincent Poitout, Miriam Cnop
Journal of Molecular Biology.2020; 432(5): 1514. CrossRef - Artemisinin and dihydroartemisinin promote β-cell apoptosis induced by palmitate via enhancing ER stress
Ke Chen, Hu Hua, Ziyang Zhu, Tong Wu, Zhanjun Jia, Qianqi Liu
Apoptosis.2020; 25(3-4): 192. CrossRef - Mechanisms of impaired pancreatic β‑cell function in high‑fat diet‑induced obese mice: The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress
Xiaoqing Yi, Xuan Cai, Sisi Wang, Yanfeng Xiao
Molecular Medicine Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids Prevent Altered-Muc2 Secretion Induced by Palmitic Acid by Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in LS174T Goblet Cells
Quentin Escoula, Sandrine Bellenger, Michel Narce, Jérôme Bellenger
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2179. CrossRef - PPAR-γ agonist, pioglitazone, reduced oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with L-NAME-induced hypertension in rats
Eman Soliman, Shereen F. Behairy, Nabila N. El-maraghy, Shimaa M. Elshazly
Life Sciences.2019; 239: 117047. CrossRef - Changes of MODY signal pathway genes in the endoplasmic reticulum stress in INS-1-3 cells
Yanan Dong, Shirui Li, Wenhui Zhao, Yanlei Wang, Tingting Ge, Jianzhong Xiao, Yukun Li, Herve Le Stunff
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0198614. CrossRef
- Nr1h4 and Thrb ameliorate ER stress and provide protection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



